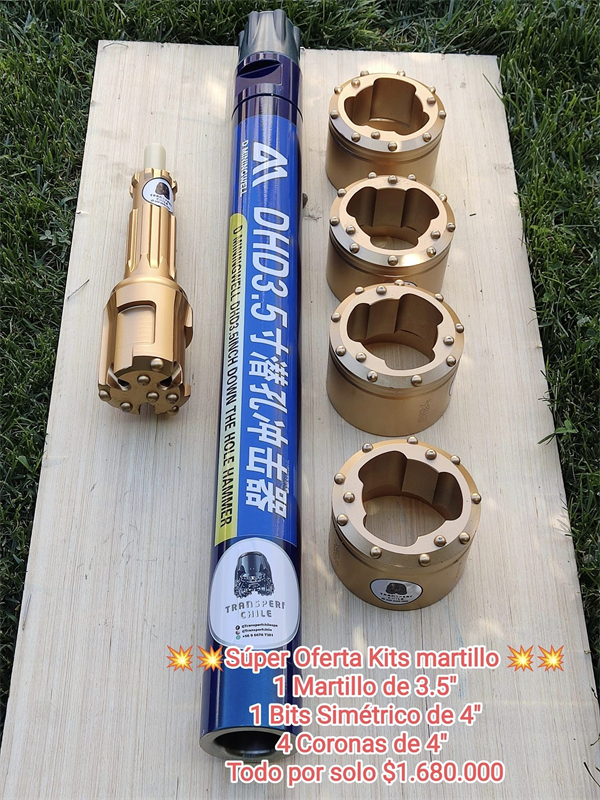
D Mininwell concentric drilling method with odex hammer
In some loose and unstable rock formations, problems such as hole collapse and burial often occur during drilling. How to avoid this series of problems? After several years of on-site practice and research, Tianhe Drilling Tools has found that concentric drilling tools have the widest applicability to formations. In addition to dealing with eccentricity and the formation conditions targeted by sliders, they can also deal with large blocks. For dry rocks, karst caves, etc., the depth of the pipe can reach about 100 meters, and the drilling efficiency of the pipe is fast, and it can also be used in the field of foundation piles.
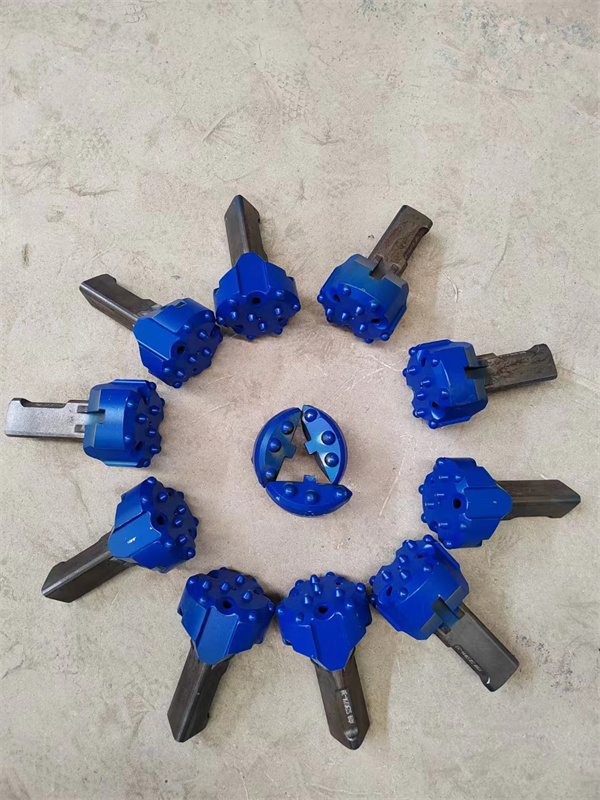
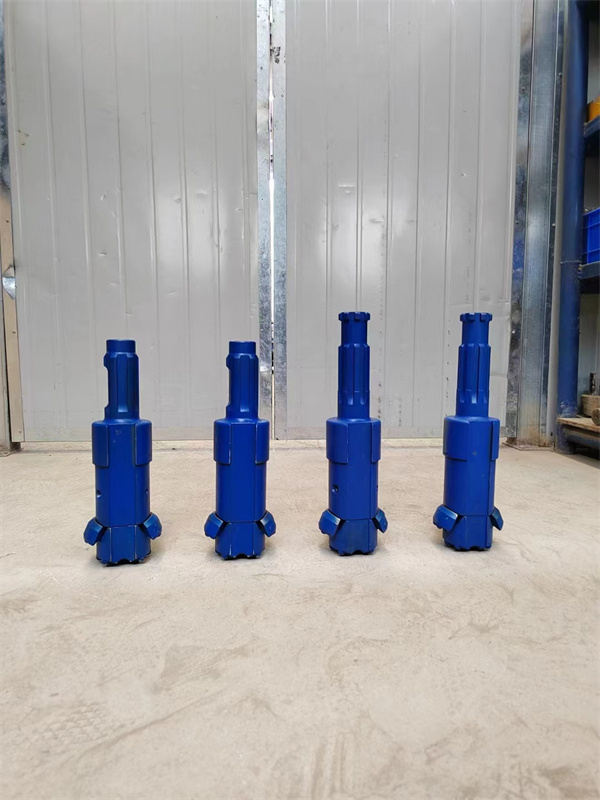
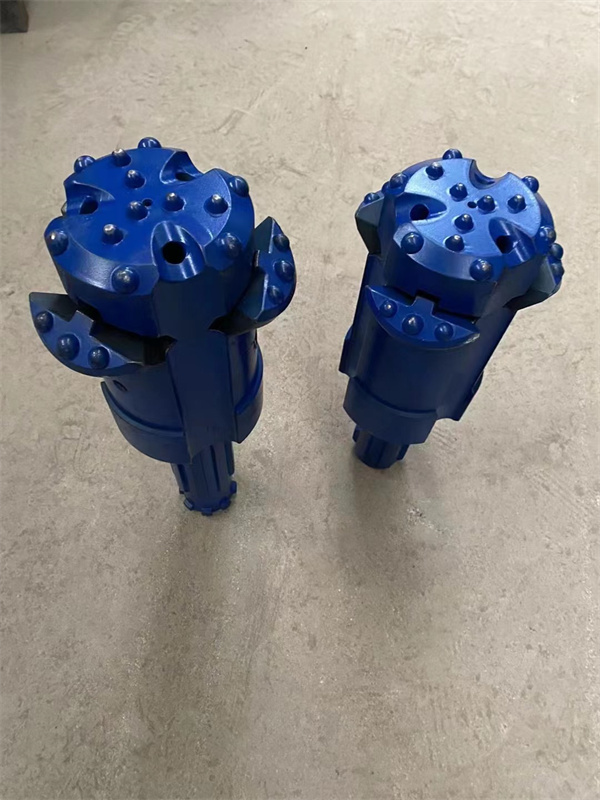
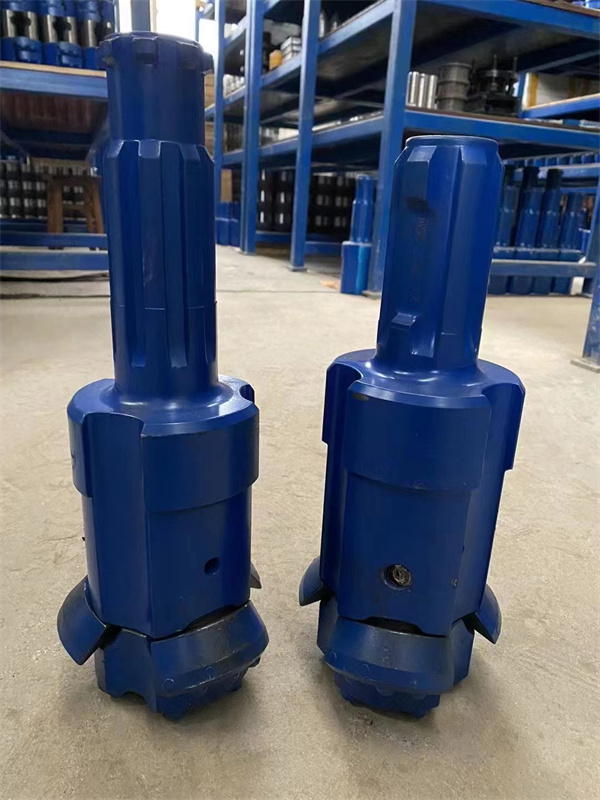
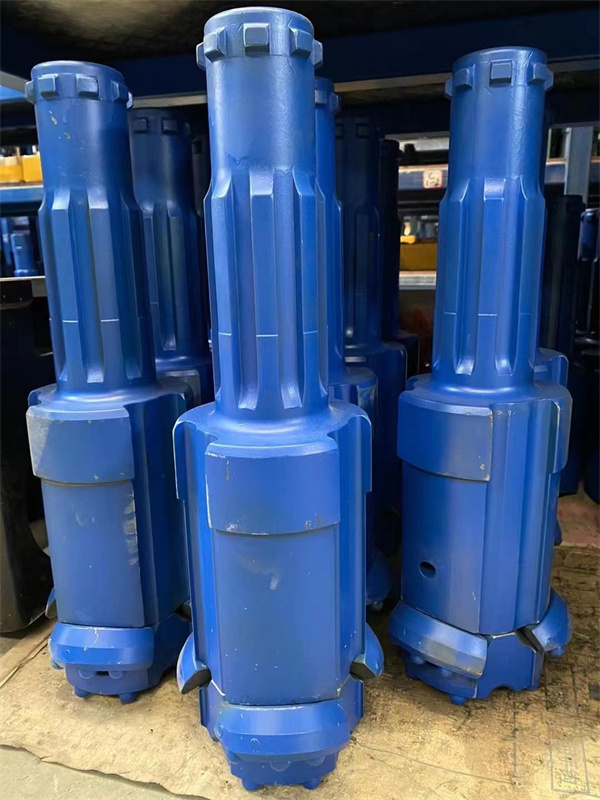
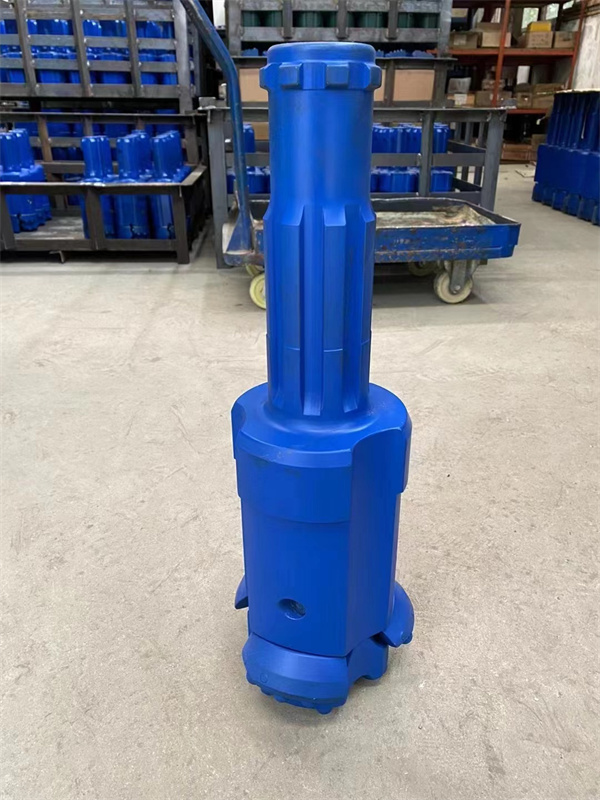
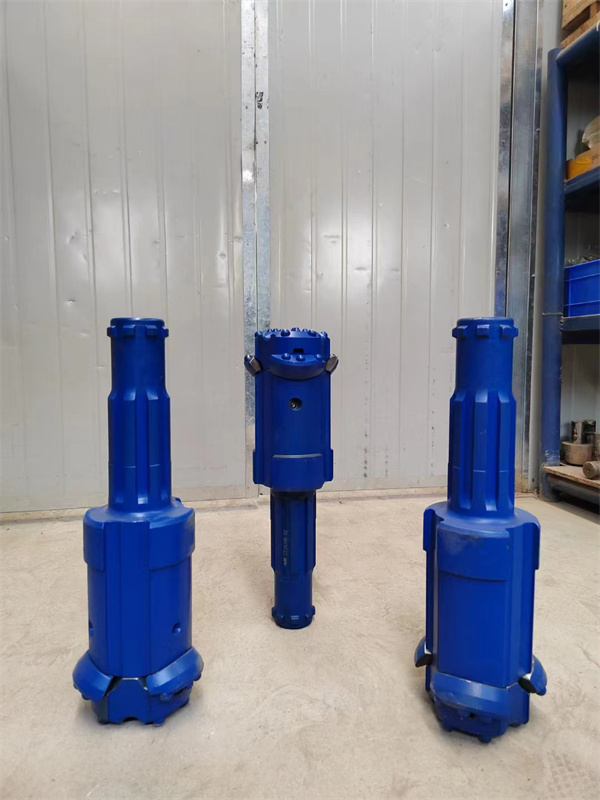
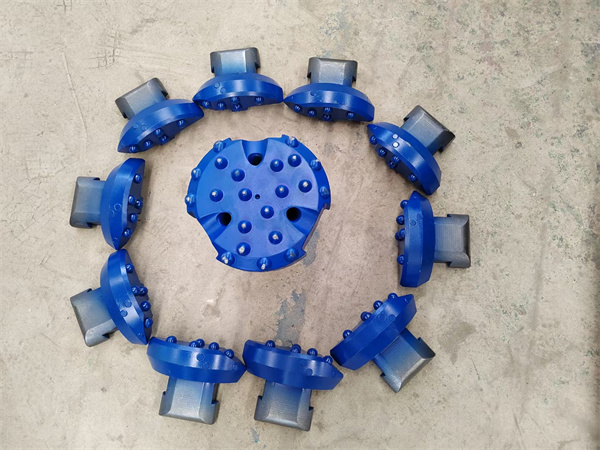
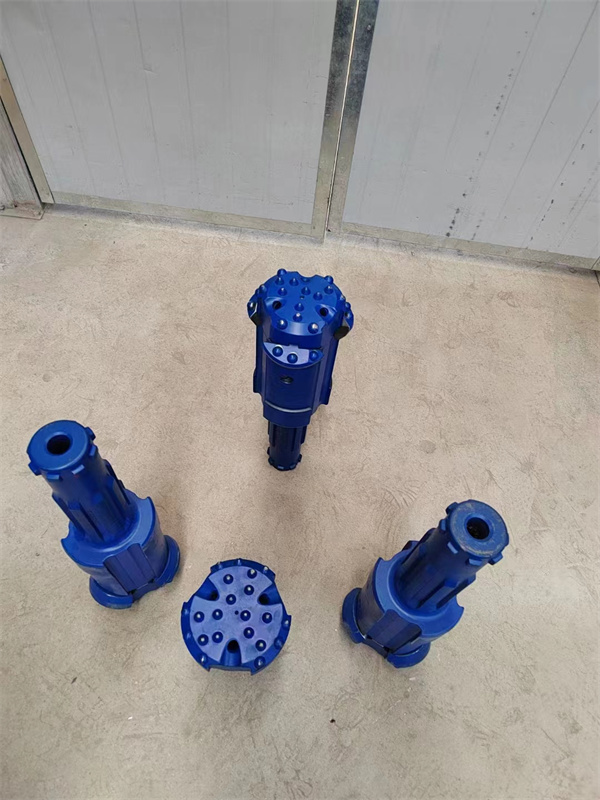
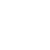
1.Structure of concentric casing system
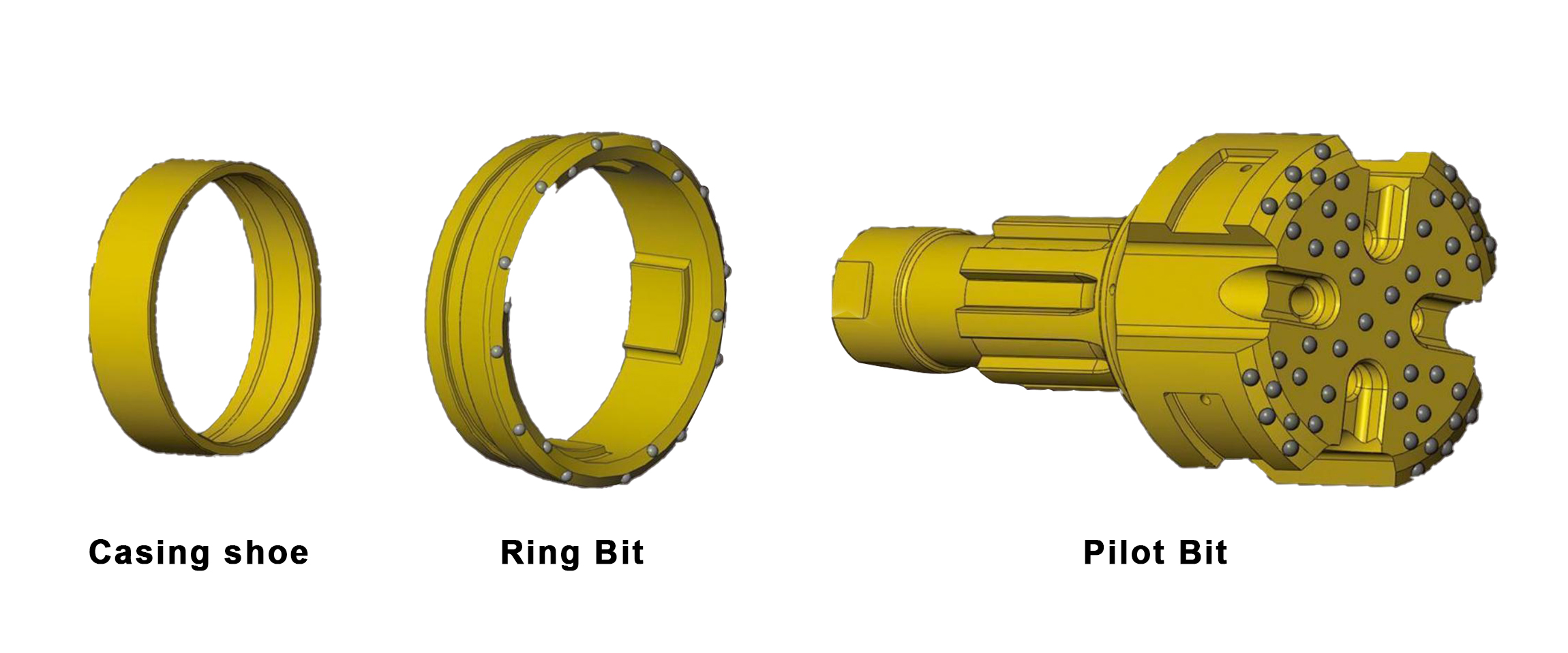
Casing shoe: Used to connect the casing tube.
Ring bit: Used to connect the pilot bit and casing shoe.
Pilot bit: The major structure of concentric casing system,with buttons and flushing grooves, etc.
2. Operation procedure
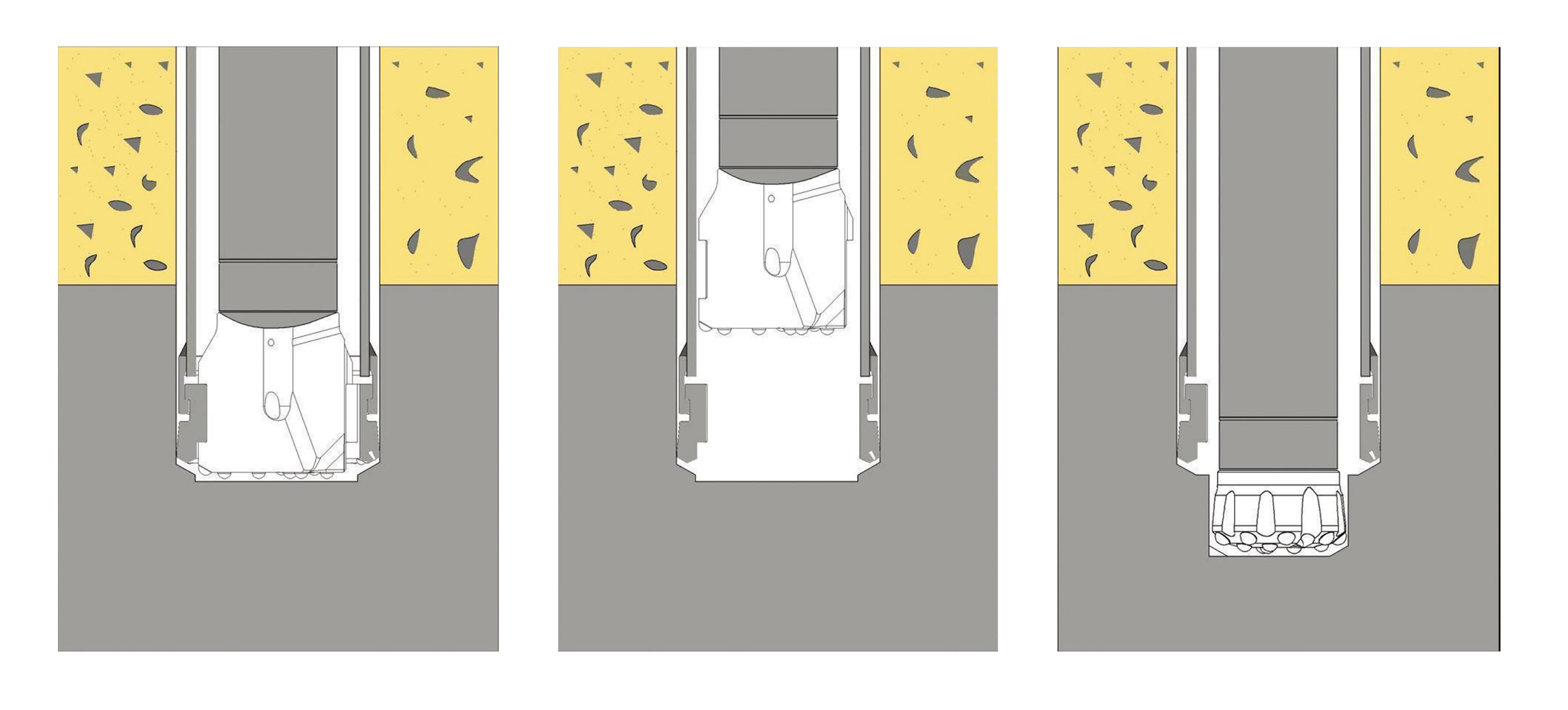
(1).Concentric system drilling through overburden
(2).Reverse rotation of the hammer and pull out the pilot bit.
(3).Replace the pilot bit to normal bit to continue drilling
3. Scope of application:
Applicable to overburden with complex dry geological conditions, such as pebbles, cracks, dry rocks, boulders, construction backfill waste, etc. Drilling holes at any angle with high straightness
The maximum hole depth can reach 150 meters
4. Structural advantages:
Straightness: Under different geological structures, the straightness of hole formation can be guaranteed
Adaptability: In complex geological structures, such as pebbles and construction waste, the drilling efficiency can be guaranteed.
Less Torque: Less torque compared to eccentric drilling system.
Easy to Unlock and Relock: Easy to relock after unlocking.
Drilling at any angle: the concentric tubular drilling tool can drill in vertical, horizontal and inclined states.
Environmental protection: Compared with eccentric drilling tools, it is more suitable for construction in urban areas because of its stable drilling, low vibration and low noise.
| Technical Parameters of Concentric drilling tools | ||||||||
| Size | OD of casing pipe(mm) | ID of casing pipe(mm) | Wall thickness | Center drill | Perforated | Allow pass | Matching DTH Hammer | Weight (KG) |
| (mm) | bit most | size | drill bit diameter | |||||
| Large outer diameter | (mm) | (mm) | ||||||
| (mm) | ||||||||
| P114/9-84 | 114 | 94 | 10 | 94 | 126 | 84 | COP34/DHD3.5/MW3.5 | 10 |
| P127/10-93 | 127 | 107 | 10 | 105 | 142 | 93 | COP34/DHD3.5/MW3.5 | 16 |
| P140/10-97 | 140 | 120 | 10 | 116 | 161 | 97 | COP44/DHD340(MW4)/SD4/QL40 | 21 |
| P146/10-110 | 146 | 126 | 10 | 124 | 165 | 110 | COP44/DHD340/(MW4)/SD4/QL40 | 22 |
| P168/12.7-127 | 168 | 142.6 | 12.7 | 141 | 188 | 127 | COP54/DHD350(MW5)/SD5/QL50/M50 | 27 |
| P178/12.7-131 | 178 | 152.6 | 12.7 | 150 | 196 | 131 | COP54/DHD350(MW5)/SD5/QL50/M50 | 32.5 |
| P194/12.7-145 | 194 | 168.6 | 12.7 | 166 | 214 | 145 | COP64/DHD360(MW6)/SD6/QL60/M60 | 42.5 |
| P219/12.7-170 | 219 | 193.6 | 12.7 | 191 | 243 | 170 | COP64/DHD360{MW6)/SD6/QL60/M60 | 58 |
| P245/12.7-195 | 245 | 219.6 | 12.7 | 214 | 268 | 195 | COP84/DHD380/(MW8)/SD8/QL80 | 78 |
| P254/12.7-203 | 254 | 228.6 | 12.7 | 224 | 276 | 203 | COP⁸4/DHD380(MW8)/SD8/QL80 | 84.5 |
| P273/12.7-223 | 273 | 247.6 | 12.7 | 241 | 298(305) | 223 | COP84/DHD380(MW8)/SD8/QL80 | 100 |
| P325/12.7-276 | 325 | 299.6 | 12.7 | 292 | 350 | 276 | COP84/DHD380(MW8)/SD8/QL8O | 135 |
| P406/12.7-350 | 406 | 380.6 | 12.7 | 377 | 442 | 350 | DHD112(MW12)/QL120/SD12/NUMA120 | 280 |
| P508/12.7-416 | 508 | 482.6 | 12.7 | 478 | 545 | 416 | QL200/SD18/NUMA180/MW18 | 522 |
| P560/12.7-475 | 560 | 534.6 | 12.7 | 528 | 595 | 475 | QL200/SD18/NUMA180/MW18 | 620 |
| P610/12.7-513 | 610 | 584.6 | 12.7 | 558 | 645 | 513 | QL200/SD18/NUMA180/MW18 | 710 |