Home » Drilling Machine » Truck mounted water well drilling rig » Operation Procedure of Truck-mounted Reverse Circulation Power Head Drilling Rig
Operation Procedure of Truck-mounted Reverse Circulation Power Head Drilling Rig
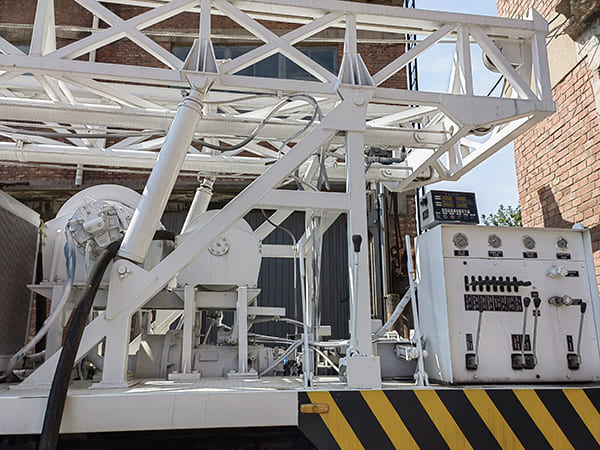
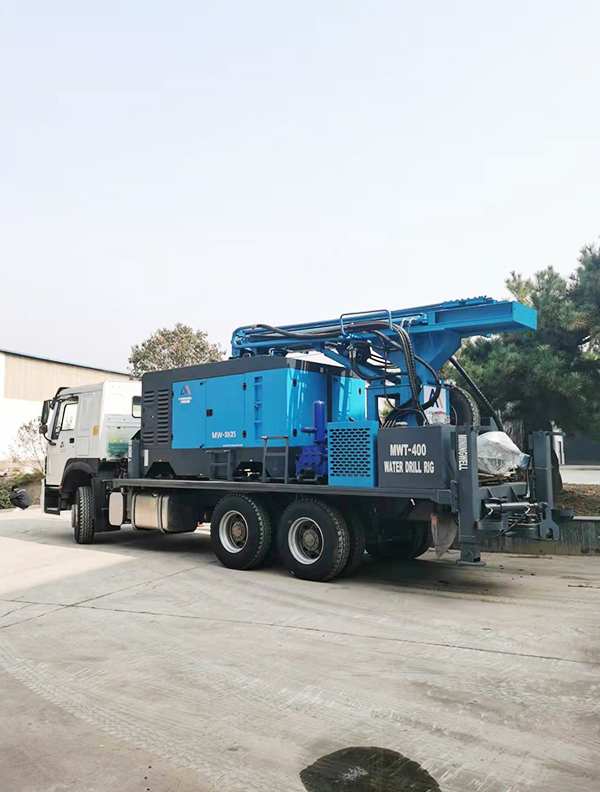
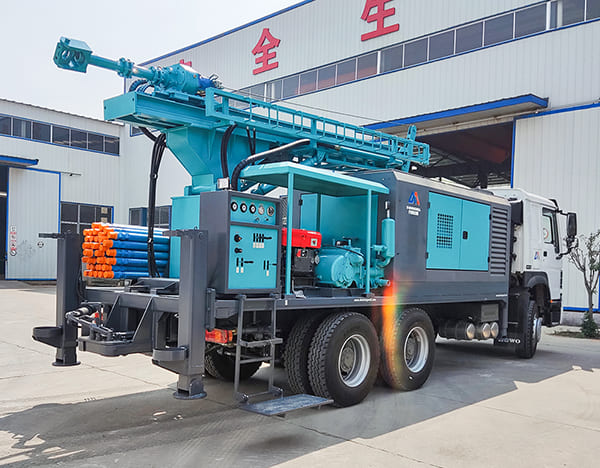
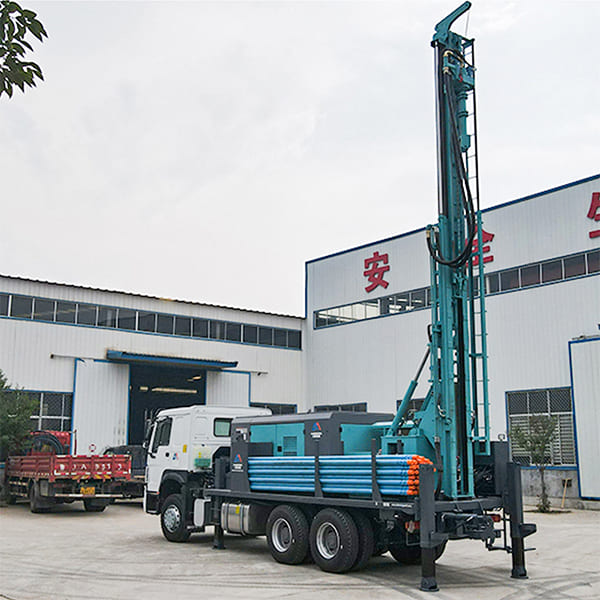
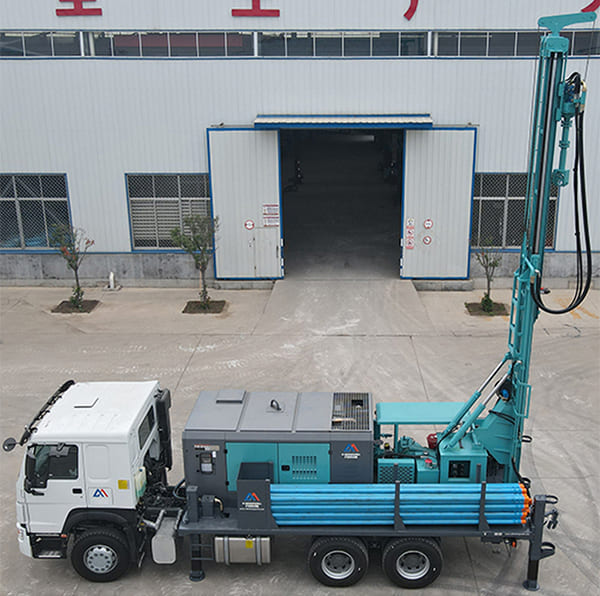
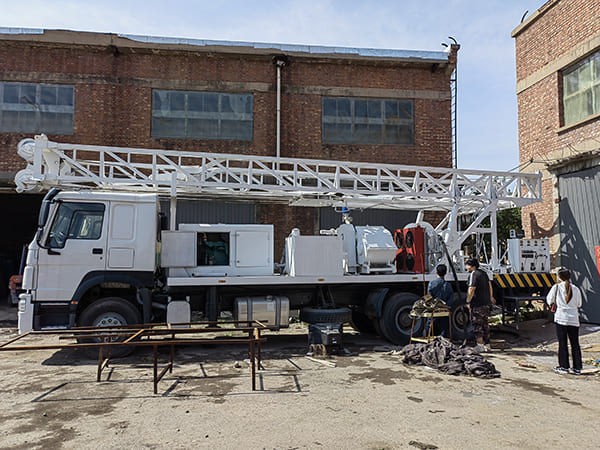
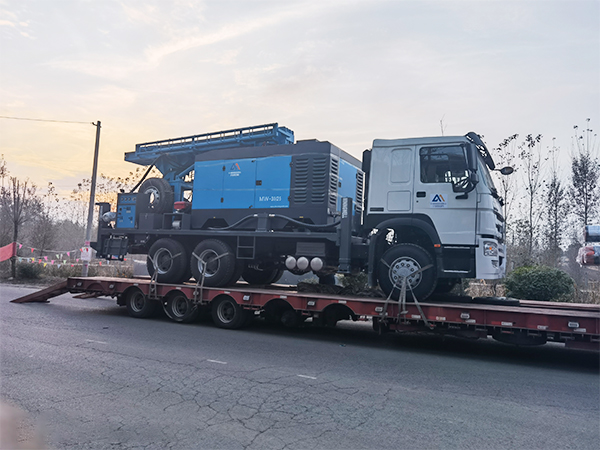
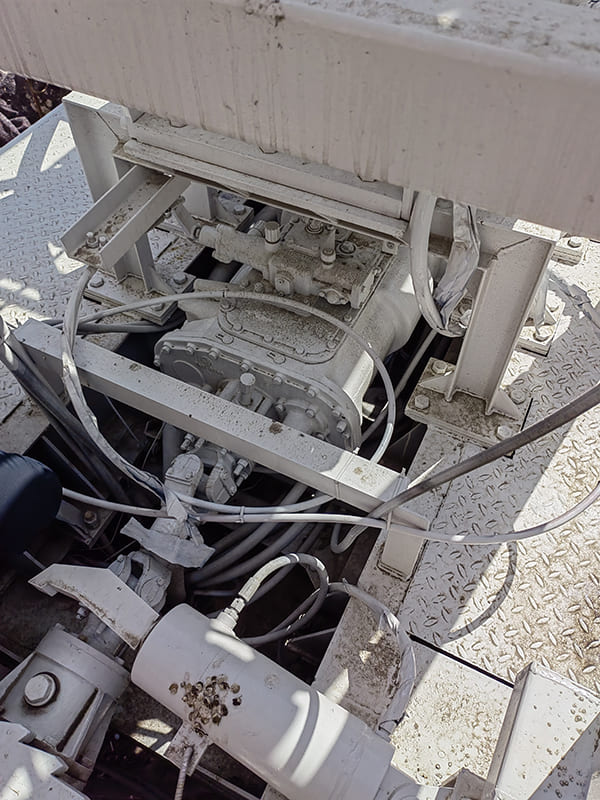
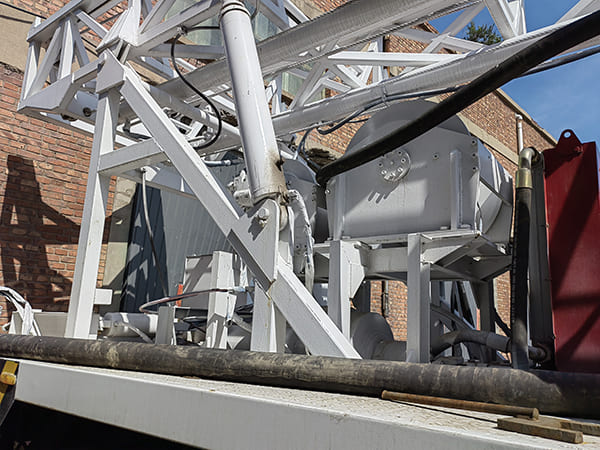
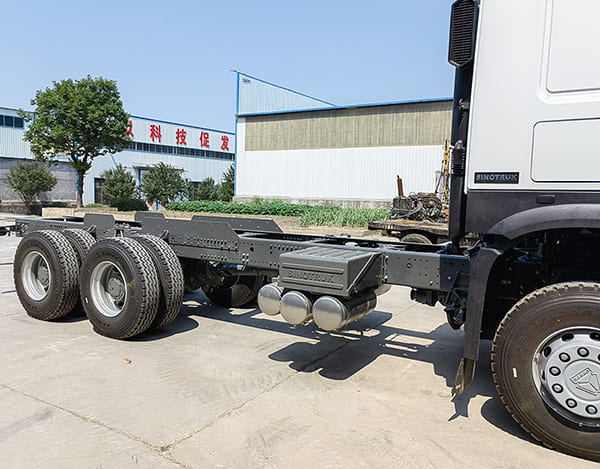
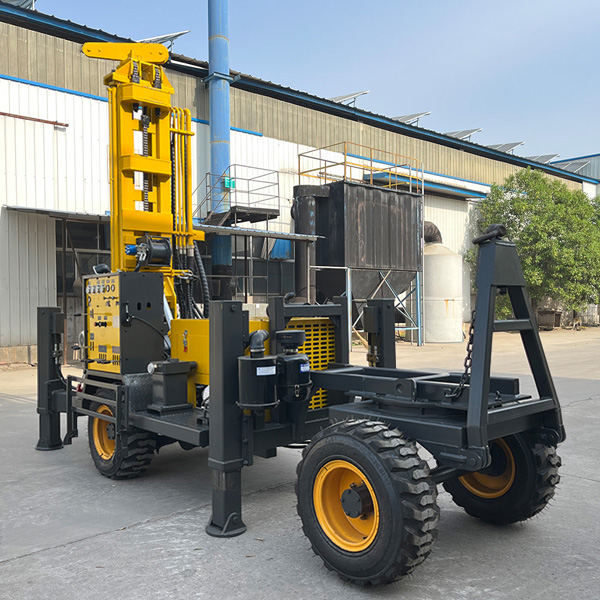
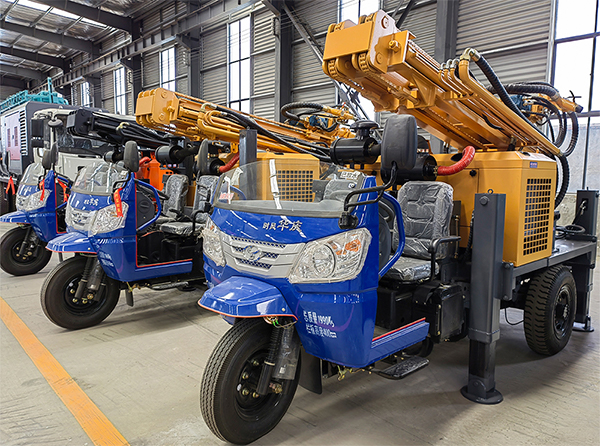
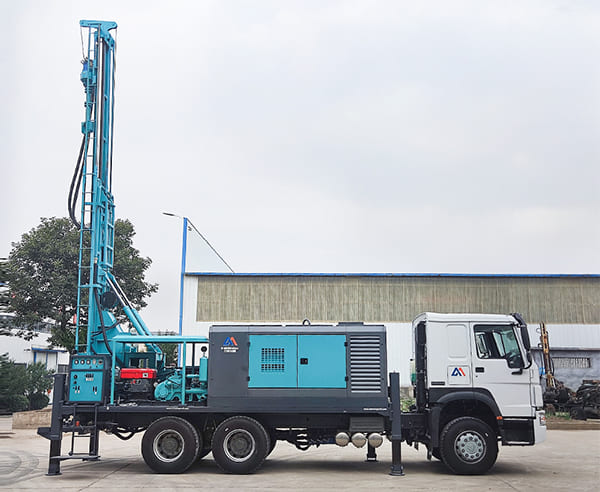
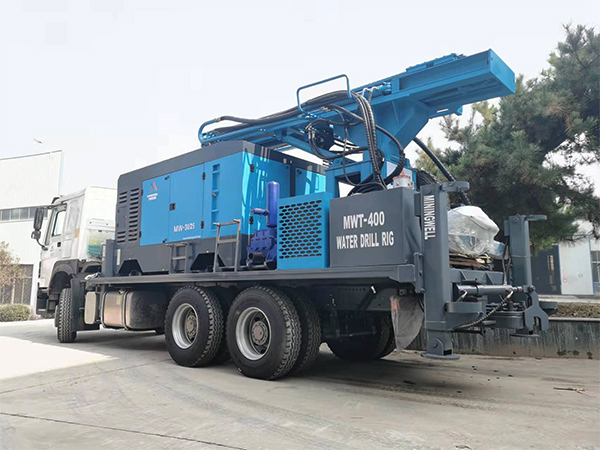
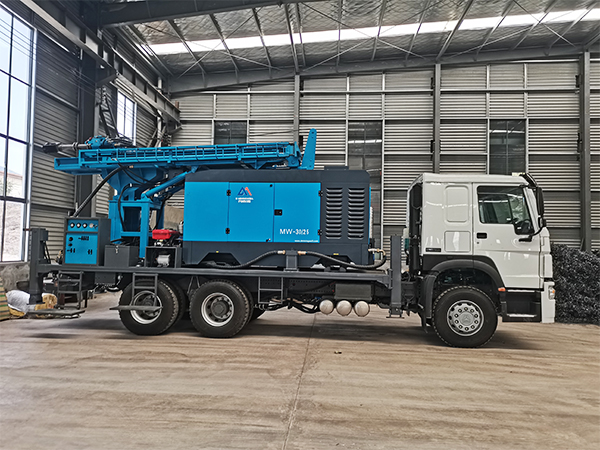
The DMiningwell MWCF200IV truck-mounted reverse circulation power head drilling rig is an independently innovative product of the factory and is a kind of truck-mounted power head rotary drilling rig. The drilling rig selects a 6X4 special drilling truck chassis and is equipped with a Yuchai diesel engine with a national IV emission standard. The diesel generator set, hydraulic system, electronic control system, vacuum pump, drill tower, etc. are all installed on the automobile chassis.
Contact US
Get Price
Share:
Content
Preparation before Construction
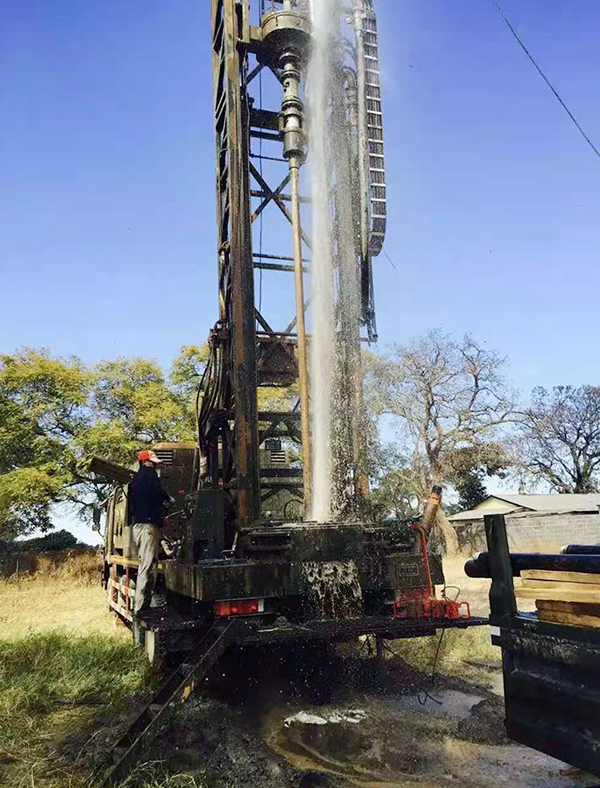
Drilling Operation
Completion of Drilling and Hole Cleaning
Pulling out the Drill Pipe and Equipment Withdrawal
Inquiry
More Truck mounted water well drilling rig